Parasitic infections are often overlooked. And the initial symptoms of worms in humans are nonspecific, so patients don't go to the doctor for a long time. As a result, patients may perceive themselves as overworked, with gastritis or poisoning, with worsening allergies or arthritis.
How to suspect the presence of a worm
The signs of worms in the body depend on the type and location of the parasite. Some symptoms appear shortly after infection. Others occur after a period of time, indicating worm migration in the body, increased intoxication, and lack of nutrients or vitamins.
The most common signs of adult worms include:
- Elevated body temperature. Fever may not be expressed - short-term up to 37. 5°C. The onset of elevated temperature coincided with a period of exacerbation, accompanied by an increase in various lymph node groups.
- One of the most common signs of the presence of worms is abdominal pain. Discomfort has a specific location—the navel, liver, or movement. The pain is accompanied by a violation of the stool, the appearance of impurities in the stool - mucus, blood. Diarrhea is more common, but obstruction can also occur due to parasites blocking the intestinal lumen.
- Anal itching is the first sign and characteristic symptom of pinworms. It happens at night and forces a person to scratch their anus.
- As the products of their decay, toxins, circulate in the body, worms can cause allergic reactions of the skin or respiratory type. So a person complains of worsening bronchial asthma, dermatitis, the appearance of eczema.
- Beriberi occurs when infected with worms. It manifests itself in the deterioration of the condition of the hair, nails, the characteristic "jam" of the corners of the mouth, and dry skin. A lack of iron in the body can lead to anemia, pale skin, and bruising under the eyes.
- The worms also have a pathogenic effect on the nervous system, so sufferers suffer from headaches, irritability, poor performance, intermittent sleep, and emotional instability.
- Worms (roundworms) that migrate through the respiratory system can cause a dry cough in humans. With the movement of the parasite in the muscles, poisoning develops, and the patient complains of pain, pain in the muscles and joints.
Notice!
The first symptoms of infection may appear within a few days after the parasite has invaded an adult's body. More commonly, 2-3 weeks from the moment of contact with parasites and migratory worms, they occur months, years later.
The combination of different symptoms doesn't clearly indicate a specific disease, but it is a reason to worry about your health and see a doctor. If a patient is self-diagnosing, looking for information on how to find out if you have a worm infection, he could lose time and develop life-threatening complications.
What are the dangers of parasitic infection
Worms in the body don't just get essential nutrients and vitamins from people. Worms poison patients with decay products, affecting internal organs. Parasites in humans can cause serious illnesses that require urgent surgery, in some cases the removal of parts of organs:
- acute intestinal obstruction;
- destruction of the integrity of the intestine with the development of peritonitis;
- appendicitis;
- Bile duct obstruction;
- eye damage.
important!
Among the delayed consequences of the invasion, leading to the deterioration of the condition and the death of the patient, are cirrhosis and liver cancer, pneumonia, pleurisy, sclerosis of the lung tissue, myocarditis, meningitis, hearing and visual disturbances, and epilepsy.
How does a worm infection happen?
To address the problem of worm prevention, it is necessary to understand the source of the parasite. The most common mechanisms of infection include: gastrointestinal, household contact, percutaneous, transmission (associated with blood-sucking insects).
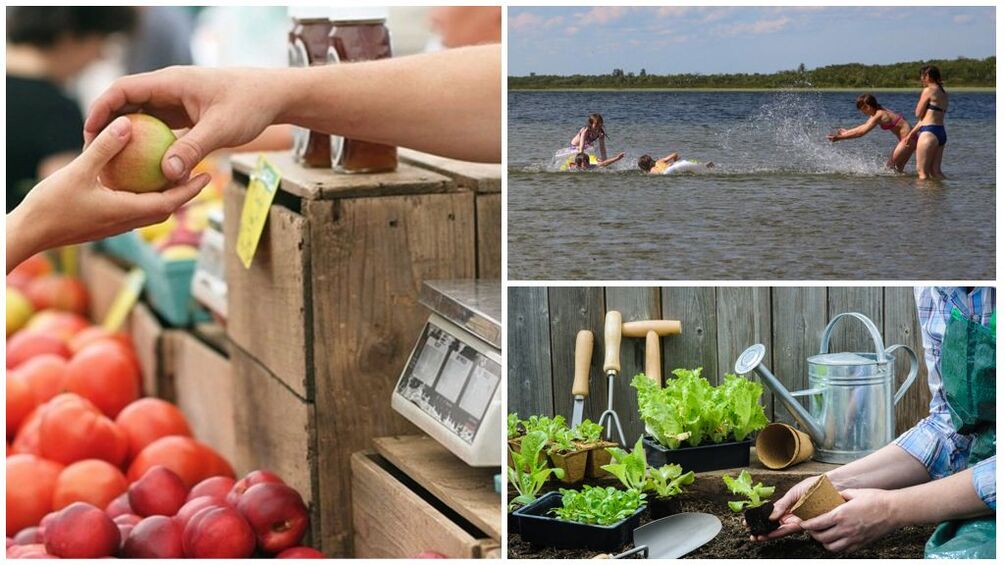

The following are the most typical situations in which worms appear in the body:
- Use vegetables, fruits, berries or vegetables contaminated with parasite eggs.
- Eat undercooked meat, fish with worm larvae. Feeding games not controlled by a veterinarian. Trichinella can therefore withstand prolonged stews and maintain their viability.
- Hygiene violation: The formal attitude of washing hands after returning from the street, touching pets or street animals.
- Bath in a reservoir containing worm larvae.
- Exposure to soil containing parasite larvae while working in the garden.
- Work in conditions with increased risk of helminth infection: children's groups, food, animal husbandry, poultry farming.
Where are the worms in the human body
There are many medical myths about the location of worms in the human body. Not all of these are based on parasitological data. Some worms occupy and reproduce in various parts of the gut. Humans may be the main host of parasites. The so-called human worms go through the sexual reproduction stage in the body and are then excreted with the feces. In the case of animal worms, humans are the intermediate host in which only the asexual (parthenogenetic) stage is possible. The parasite spreads to the internal organs, causing damage to them. So worms in humans can be detected:
- under the skin;
- in the liver;
- in the bladder;
- in the eyes;
- in the muscles;
- in the lungs and heart;
- in the brain.
If we consider the description of the worm's life cycle in the form of a photograph with an explanation, we can track its migration through the body and guess what the main symptoms of the disease will look like.
Diagnosis of Worms
Blood images of abdominal pain, fever, rash, expectoration, inflammation and allergic changes are the basis for checking a person for parasites. Infectologists recommend laboratory tests to detect the worm or the immune response to it in the body.
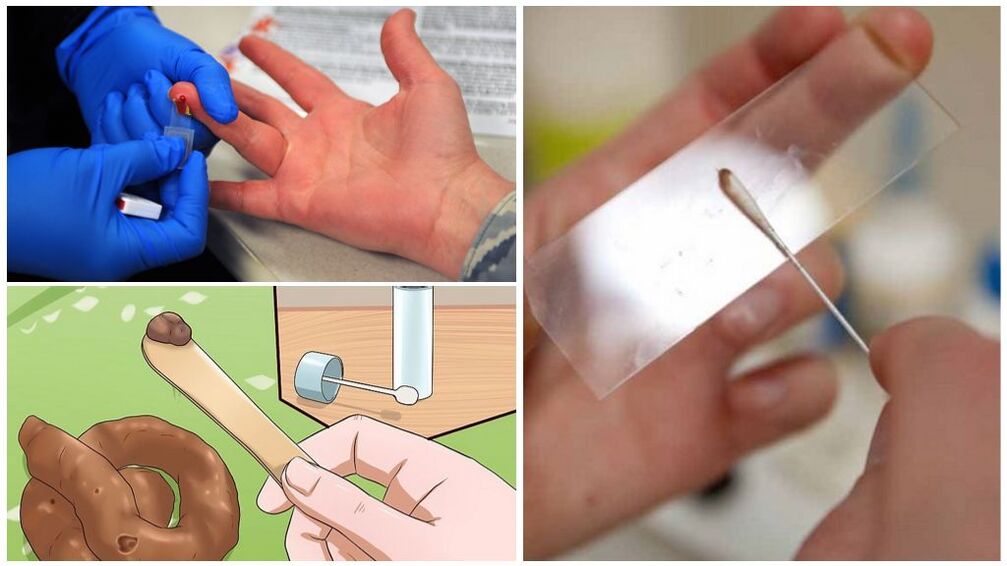

The following methods can help identify worms in the human body:
- analysis of parasite eggs in feces;
- Scraping or smearing for enterobiasis;
- Immunological tests to detect antibodies to worms;
- PCR analysis of worm DNA fragments;
- Detection of worms in duodenal contents, tissue biopsy specimens.
These methods will help find out the type of parasite and choose effective drugs. If the internal organs are damaged, the following will help diagnose the worm:
- chest X-ray;
- Ultrasonography of the liver, heart, and pancreas;
- cystoscopy;
- Brain MRI.
Infectious disease specialists refer neurologists, ophthalmologists, cardiologists, and urologists for consultation if needed.
Notice!
Instead of trying to identify the worm yourself, you should turn to "unique computer diagnostics" outside of a medical facility. This leads to the loss of time and the deterioration of health.
Treatment of human worms
If an illness is detected, an infectious disease specialist will give comprehensive advice on treatment, regimens and diet for the illness. If necessary, the doctor will recommend hospitalization. There is no single "magic" drug for worms, and symptoms and treatment of worms in adults can vary.
You need to understand the basics of parasite treatment:
- To fight worms, drugs are used. The choice of treatment regimen (dose, duration, frequency of administration) depends on the type of worm and the physical condition of the patient.
- In severe cases, assistance will be provided in a hospital setting.
- You should not reduce the dose alone, reducing the duration of treatment with the tablet or worm suspension.
- Some medicines require a diet and refusal to drink alcohol.
- There is no "magic" remedy that will get you rid of any worms quickly in 1 day. It is true that short courses of treatment are used to treat some worms in the human body, but it is impossible to eliminate all the parasites in the body with a single tablet, tincture or ointment.
- Herbal preparations are used for patients, and for health reasons, medicines in the form of tablets or suspensions are contraindicated.
- Antiallergic drugs, hepatoprotectants, intestinal adsorbents, and immunomodulators are prescribed as adjuvant therapy. They do not by themselves help clear worms from the body, but can improve a person's overall health and eliminate unpleasant symptoms of disease and side effects of treatment.

important!
Folk remedies are only used as adjunctive treatments. The stand-alone use of alternative medicines is fraught with exacerbations.
Pharmacy Fund
Treatment with drugs from the anthelmintic group helps to eliminate and expel parasites from the body. Medications have different application points:
- disrupts the absorption of nutrients by parasites;
- disrupt the metabolism of the worm;
- Causes paralysis of the worm's muscle tissue.
Notice!
With proper use and prevention of helminthiasis in the future, worm therapy can indeed help to permanently clear a person of parasites from their gut and internal organs. However, if a patient ignores basic hygiene rules, they can become reinfected with the parasite.
Additionally, infectious disease specialists can prescribe herbs that help poison and repel human worms. Your doctor will recommend certain herbs based on information about your physical condition and type of parasite. To heal the sick, apply: pumpkin seeds, tansy grass, and centaurs.
Folk treatment for roundworms
Many patients reject traditional treatments and want the help of traditional medicine. Attempting to clear the worms at home with questionable solutions, infusions, can lead to increased poisoning and allergic reactions, infectious disease specialists warn. If the time is missed, the disease progresses and a fatal outcome is possible.
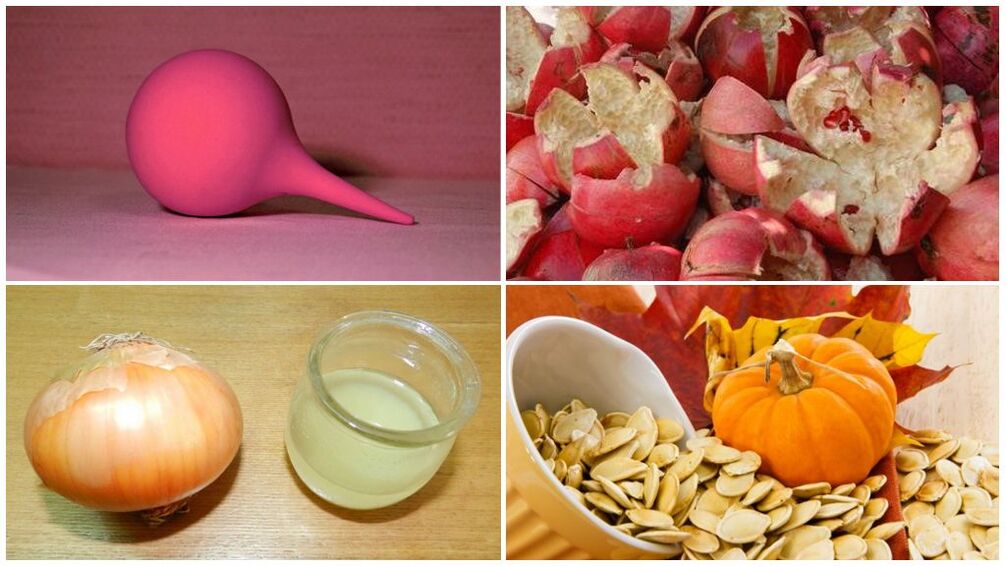

To drive the worms out of the body, the following home remedies are widely used:
- onion soup;
- pomegranate peel;
- Enema and ingestion of pumpkin seeds;
- Unsweetened vegetable and physalis juices;
- garlic with milk;
- soda enemas;
- Wormwood tincture.
Treatment Reviews
Before starting a course of treatment, patients consider various options for dealing with parasites, trying to understand how to properly poison the worms. In their review, people who have been infected with the worm describe traditional drug therapy as a fairly effective method. Getting rid of worms with folk remedies is extremely rare.
- "I started to worry about anal itching. Sent to therapist and received instructions on scraping. Finding pinworms in scraping is very unpleasant. I read about how dangerous the worms are and decided not to poison myself with self-medication. On the doctor's advice, she took a dewormer - 1 tablet once a week. The course lasted 2 weeks and I immediately felt relieved and the itching went away. I'm sure it wasn't such a terrible infection, butThe drug was "very good".
- "I got worms after eating fish at a party. Diarrhea soon started. I lost weight and my skin became dry and itchy. Later I studied in detail how to treat parasites and how to restore my body, IStarted taking anthelmintics on my own. I was embarrassed to go to the doctor. Medications didn't help. I tried folk methods to fight worms: I cleaned my liver with bitterness, drank garlic milk and enemas. But it didn't get better. I had to ask for helpAs an infectious disease specialist, I was being treated with a benzimidazole-based dewormer. By the time I 'mature' went to the doctor, I lost 4kg, pale and nervous. "
prevention
Knowing how worms appear in the body allows anyone to protect themselves and their loved ones from infection. Prevention includes:
- Wash hands with soap after contact with animals and go home.
- Deworm your pets regularly.
- Change bed linen promptly.
- Wet-wash, ventilate, and clean carpets and upholstered furniture regularly.
- Eat meat that has been controlled by a veterinarian.
- Thorough heat treatment of meat and fish.
- Refuse to eat raw meat, fish and offal.
Infected worms require immediate treatment. You should watch for the following symptoms: diarrhea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, weight loss, rash, cough, fever, and seek immediate medical attention. After treatment, precautions should be taken to prevent reinfection.